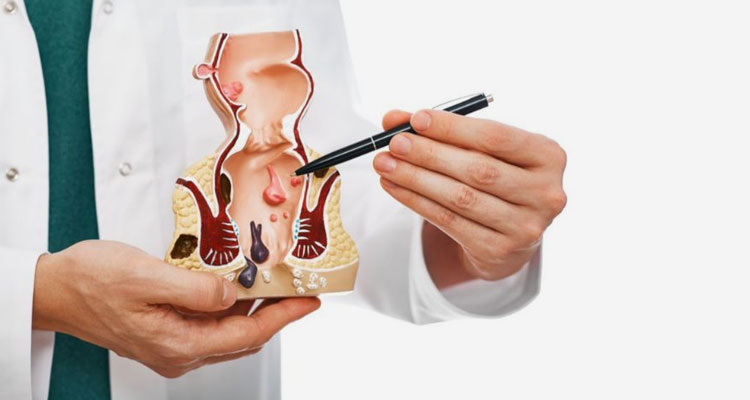
What is an anal fissure?
An anal fissure is a tear in the lining of the anal canal. It often occurs after the passage of a hard bowel movement.
What are the symptoms of an anal fissure?
An anal fissure typically causes pain, especially with a bowel movement. Sometimes, bleeding occurs as well.
How is an anal fissure diagnosed?
An anal fissure can be seen by a doctor on a visual exam of the anal region or can sometimes be felt by the doctor on an exam if it is not visible. If the fissure is touched, it will usually be painful. Sometimes an endoscope (see above) is used to look inside the anal canal a very short distance to see how far the tear extends.
Can anal fissures be prevented?
Since anal fissures often result from the passage of hard bowel movements, keeping the stools soft and bulky (with fiber supplements) may help prevent them from occurring in the first place.
How are anal fissures treated?
Most anal fissures will heal on their own within a few weeks if the stools are kept soft (possibly with stool softeners, and fiber supplements) and the area is not repeatedly re-injured.
Other measures may include:
- Sitz baths: These will soothe the affected area with water
- Medicated creams and/or suppositories to relieve pain and inflammation
- Occasionally, the use of nitroglycerine or diltiazem-ointment applied to the area will be necessary
- Occasionally, injection of botulinum toxin, Botox®, may be helpful
- Surgery may be necessary if symptoms persist. The operation involves partially cutting a muscle that regulates the passage of stool out of the rectum. Cutting this muscle relieves pressure on the skin near the fissure, and allows the fissure to heal. (Lateral anal sphincterotomy)