Overview
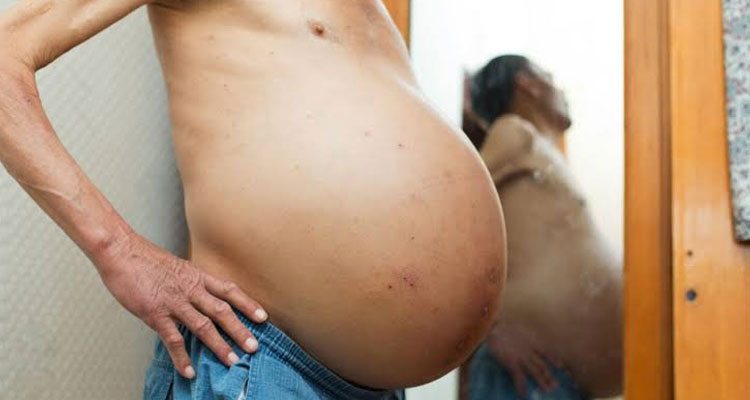
The accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity is called ascites. Although it can occur from various health problems, ascites are common in patients with cirrhosis, which is significant scarring of the liver. Often, the development of ascites indicates serious liver disease and patients should be referred to a liver specialist.
Causes
Cirrhosis of the liver is the most common cause of ascites, but other conditions such as heart failure, kidney failure, infection, or cancer can also cause ascites. Ascites are most commonly caused by a combination of increased pressure in the blood vessels in and around the liver (portal hypertension) and a decrease in liver function.
Symptoms
Most patients who develop ascites notice abdominal distension and rapid weight gain. Some people also develop swelling of ankles and shortness of breath. Additional symptoms or complications, listed below, may also occur.
Abdominal pain, discomfort, and difficulty breathing: These may occur when too much fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity. This may limit the ability to eat, ambulate and perform activities of daily living.
Infection: This is called spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) and it usually causes abdominal pain, tenderness, fever, or nausea. If not promptly diagnosed or treated, patients may develop kidney failure, severe infection in the bloodstream, or confusion. The diagnosis is generally made by taking a sample of the fluid from the abdominal cavity. This infection is treated with intravenous antibiotics, and, after recovery, patients often require treatment with oral antibiotics to prevent infection from recurring.
Ascites-related hernias: Elevated intra-abdominal pressure can lead to the development of umbilical (around the belly button) and inguinal (groin) hernias that can cause abdominal discomfort. Surgical repair is generally avoided unless there is severe pain suggesting the intestines or tissue may be pinched or twisted along with a persistent bulge from the hernia. Surgeons who have experience in treating patients with cirrhosis should perform these operations.
Fluid accumulation in the chest: This is called hepatic hydrothorax and the abdominal fluid fills into the lung cavities (mostly on the right side) in addition to the abdominal cavity. This condition may result in shortness of breath.
Risk Factors
In general, the development of ascites indicates evidence of advanced liver disease. However, blood clots in the vessels in and around the liver, as well certain types of tumors in the abdomen can also cause ascites. Tuberculosis is one of the major infectious causes of ascites in India. Certain types of cancer like stomach cancer, esophageal cancer, ovarian tumors, liver cancer, etc. can also cause ascites.
Screening/Diagnosis
Depending on how much fluid is present in the abdomen, ascites may be diagnosed on physical examination but is usually confirmed by tests such as ultrasound or CT scan of the abdomen. In the majority of patients, the doctor will recommend that a small needle be inserted through the abdominal wall (after local anesthesia) to remove fluid to be examined in the laboratory. This test is called paracentesis. The fluid removed will be examined for signs of infection or cancer and to determine the cause for the fluid accumulation.