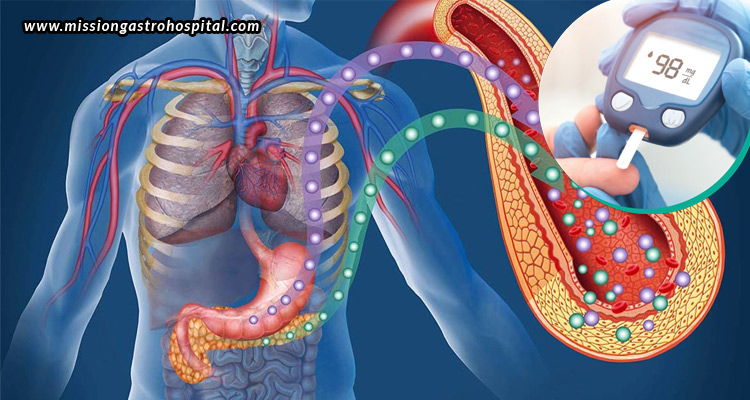
In recent years, the significance of gut health has become increasingly prominent in medical and nutritional discussions. While it is often linked to digestion and nutrient absorption, the gut serves many additional functions beyond food processing. It is crucial in regulating the immune system, controlling inflammation, and impacting chronic diseases such as obesity and diabetes. A particularly intriguing discovery in contemporary medicine is the strong relationship between gut health and diabetes, particularly how the gut microbiome influences insulin resistance, glucose metabolism, and the likelihood of developing diabetes. This blog will delve into how your gut and its microbial inhabitants can determine your metabolic health, along with strategies to foster a gut-friendly and diabetes-resistant lifestyle.
How the gut affects blood sugar levels
- Microbiota and insulin sensitivity
Specific gut bacteria influence the sensitivity of your cells to insulin. A healthy microbiome generates short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as butyrate, through the fermentation of dietary fibres. These SCFAs improve insulin sensitivity by decreasing inflammation, aiding gut barrier integrity, and regulating hormones related to appetite and glucose management. Individuals with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes often have reduced levels of butyrate-producing bacteria, indicating that an imbalance in gut bacteria may hinder glucose regulation.
- Inflammation and metabolic dysfunction
When the integrity of the gut barrier is compromised, substances like lipopolysaccharides (LPS) can enter the bloodstream. This results in an immune response and persistent low-grade inflammation, which is a significant factor in the development of insulin resistance. Inflammatory cytokines disrupt insulin signalling, hinder glucose absorption by cells, and contribute to increased blood sugar levels.
- Gut hormones and appetite control
The gut interacts with the brain through the gut-brain axis, affecting appetite and metabolism through hormones such as GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1), which boosts insulin secretion and curbs appetite; PYY (Peptide YY), which enhances feelings of fullness and delays gastric emptying; and ghrelin, often referred to as the “hunger hormone,” which triggers the sensation of hunger. A balanced gut microbiome is essential for regulating the release of these hormones, thus aiding in appetite control and improving blood sugar management.
Signs your gut health might be affecting your blood sugar
- Ongoing bloating or inconsistent bowel habits
- Persistent fatigue or cognitive cloudiness
- Cravings for sugar or frequent feelings of hunger
- Weight increase particularly in the abdominal area
- Dermatological problems such as acne, rashes, or eczema
- Repeated occurrences of yeast infections or a history of antibiotic overuse
Although these symptoms do not ensure the onset of diabetes, they serve as significant indicators that your gut health requires improvement.
Improving gut health to manage and prevent diabetes
- Increase your fibre intake
Incorporating dietary fibre into your meals nourishes beneficial gut bacteria and enhances digestion. Strive for a daily intake of 25–30 grams of fibre by adding whole grains such as oats, brown rice, and barley; legumes like lentils, chickpeas, and black beans; vegetables including broccoli, spinach, and carrots; and fruits such as apples, pears, and berries. These fibre-dense foods foster a diverse and robust gut microbiome.
- Incorporate prebiotic and probiotic foods in your diet
Probiotic-rich foods introduce helpful bacteria into the digestive system. Excellent sources include yogurt with live cultures, kefir, fermented vegetables like kimchi and sauerkraut, and soy products such as miso and tempeh. Conversely, prebiotic foods nourish and promote the growth of beneficial bacteria already present. These consist of garlic, onions, leeks, bananas, and asparagus. Incorporating both food types into your diet contributes to a balanced and flourishing gut environment.
- Limit your intake of processed foods and sugars
Reducing the consumption of highly processed foods, artificial sweeteners, and refined sugars is crucial for gut health. These elements can harm the gut lining, foster the growth of harmful bacteria and yeast, and lead to dysbiosis. Additionally, high-sugar diets can exacerbate insulin resistance, complicating blood sugar control.
- Engage in regular physical activity
Consistent exercise not only improves insulin sensitivity but also promotes gut health by enhancing microbial diversity. Engaging in just 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, five days a week can significantly benefit both metabolic and digestive health.
- Manage stress levels
Chronic stress adversely impacts gut flora and triggers inflammation throughout the body. To foster a healthier gut and overall wellness, integrate stress-relief techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, and a regular sleep routine. Effectively managing stress is vital for preserving the delicate balance of the gut microbiome.
When to see a professional
Chronic symptoms such as bloating, constipation, or fatigue, particularly when accompanied by fluctuations in blood sugar, may signal underlying issues like dysbiosis or leaky gut. Consulting a specialist is essential! Mission Gastro Hospital is a reputable provider of digestive care, featuring the best gastro doctor Ahmedabad. Equipped with advanced diagnostic tools and tailored care plans, the hospital assists in evaluating gut health, managing digestive disorders, and enhancing metabolic wellness.
Your gut serves not only as a digestive organ but also as a crucial metabolic centre influencing your blood sugar levels, immune response, and overall health. Whether your goal is to manage diabetes or prevent its onset, supporting your gut microbiome is one of the most effective actions you can take. Emphasize a diet rich in fibre, minimize inflammation, maintain regular physical activity, and seek professional guidance when necessary. The link between gut health and diabetes is clear; it’s time to take action. Care for your gut, and it will support your well-being.