What is the rectum?
The rectum is the last few inches of the colon. The rectum is connected to the anal canal, which leads the fecal matter out of the body. The opening is called the anus. Problems in this part of the body are common, but people are often embarrassed to seek help. Common symptoms may include bleeding, pain, and itching. When symptoms are persistent, it is important to have an evaluation by a doctor.
What are hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are blood vessels (veins) in the rectum or anal canal. When those blood vessels become swollen or dilated, symptoms may develop. Many people have hemorrhoids but have no symptoms.
How common are hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are very common and by age 50, nearly half of Americans have hemorrhoids. Nearly 5% of the US population (15,000,000 people) has sought medical care for symptomatic hemorrhoids. Many more have problems with hemorrhoids but never seek formal medical attention.
What are the different types of hemorrhoids?
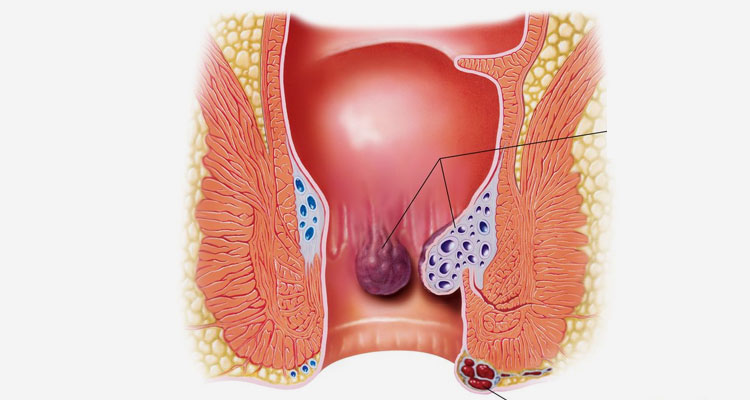
External hemorrhoids are dilated veins covered by the skin near the anal opening. They may be felt as bumps or lumps near the outside of the anus, and become painful when they are swollen with blood. They can sometimes be confused with skin tags which are extra pieces of skin near the anus
Internal hemorrhoids are dilated veins that form inside the rectum and above the anal opening, and are therefore “internal”. However, in some situations, they may enlarge and protrude (prolapse) out of the anus.
What are the symptoms of hemorrhoids?
External hemorrhoids may be present and cause no symptoms. When they cause symptoms, the most common are pain or itching; they can often be felt as a bulge in the skin near the anal opening.
Internal hemorrhoids may be present and cause no symptoms. When they cause symptoms, the most common is painless rectal bleeding, which usually is seen as bright red blood on the toilet paper or in the toilet bowl. It is important to know that just a few drops of blood in toilet water can change the color of the water dramatically. Other symptoms are itching, pain/soreness or feeling tissue come out when having a bowel movement.
How do hemorrhoids occur?
Hemorrhoids may develop as a result of repeated straining to have a bowel movement, sometimes as a result of longstanding constipation or diarrhea. They are also seen commonly in any condition that leads to increased pressure inside the abdomen. Common examples would include pregnancy and lifting heavy weights.
How are hemorrhoids diagnosed?
Hemorrhoids are suspected when they produce the characteristic symptoms listed above. External hemorrhoids may occasionally be seen on visual examination of the anus. A full exam usually includes a digital rectal exam, where the doctor will insert a gloved finger into the rectum. Internal hemorrhoids may be identified on external exam if they protrude with straining or may be detected during a check with a flexible or rigid tube with a light and a camera that is inserted in order for the doctor to see the inside of the anal canal and lower rectum. Alternatively, your doctor may insert a small plastic speculum to exam the rectum. The speculum is called an anoscope and the flexible tube is a sigmoidoscope.
How are hemorrhoids treated?
Most hemorrhoids resolve spontaneously, or with simple measures. These measures include avoidance of straining, and treatment of hard stools or constipation with increased fluids, addition of increased fiber in the diet or taken as fiber supplements and stool softeners or lubricants. Soaking the affected area in a hot bath or using a sitz bath are also very effective. There are multiple over-the-counter creams and suppositories which can reduce symptoms of itching and pain. When these are not effective, your doctor may prescribe a steroid cream or suppository to use for 1-2 weeks. Some people find cleaning the anal region with a moist towel or “baby wipe” after a bowel movement to be soothing. It is important to remember that hemorrhoids commonly recur with people and that you may have no symptoms in between episodes.
In some circumstances, hemorrhoids that do not resolve or bleed repeatedly need other types of treatment. These include:
- Rubber band ligation: Small rubber bands are placed around the hemorrhoids, often in a doctor’s office. This will cause hemorrhoid(s) to fall off in several days and form a small ulcer where the hemorrhoid was. This heals over time. This is generally a painless procedure and minor discomfort resolves in 24 hours. Using a pain reliever like Tylenol, Aspirin or Ibuprofen helps to remove discomfort after the procedure. The procedure is safe and has become common for a gastroenterologist to do at an office visit.
- Infrared coagulation: A small probe is inserted in the rectum and heat is applied to destroy hemorrhoid. This should be mostly pain-free.
- Sclerotherapy: A chemical is injected directly into hemorrhoid to help destroy the hemorrhoid tissue.
- Surgery: Removal of the dilated, stretched veins. This is performed by a general or colorectal surgeon in an operating room.