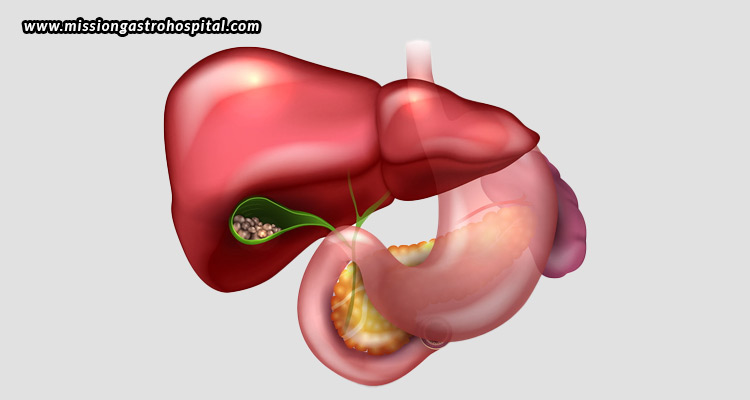
Millions of individuals worldwide suffer from gallstones, a common medical condition for which many people are ignorant of the causes, signs, and available treatments. These tiny, pebble-like deposits develop in the gallbladder, a little organ beneath the liver that holds bile, a substance the liver produces to help with digestion. Gallstones can be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball, and their presence can result in mild to severe symptoms or, in certain situations, no symptoms at all. The causes of gallstones, their detection methods, accessible therapies, and preventative advice for food and lifestyle modifications will all be covered in this blog.
Causes of gallstones
Gallstones develop when bile components such as bilirubin or cholesterol solidify into particles. The most prevalent kind, cholesterol gallstones, are caused by excess cholesterol, whereas pigment gallstones, which are frequently associated with liver illness or blood abnormalities, are caused by excess bilirubin. Gallstones develop when the liver excretes more cholesterol than bile can breakdown. This excess cholesterol crystallises. Gallstones can also form as a result of the liver producing too much bilirubin due to medical illnesses like liver cirrhosis or blood disorders like sickle cell anaemia. Bile also gets concentrated if the gallbladder does not empty correctly or often enough, which raises the risk of gallstone development.
Risk factors for gallstones
Several factors can increase the risk of developing gallstones. Women are more prone to gallstones than men due to hormonal factors like estrogen, which raises cholesterol levels in bile. Age also plays a role, with the risk increasing, particularly after age 40. Obesity is another contributing factor, as excess body weight raises cholesterol levels in bile and reduces gallbladder function. A diet high in fat, cholesterol, or refined carbohydrates and low in fiber can further elevate the risk. Additionally, family history and genetics may influence gallstone formation. Pregnancy can also lead to gallstones due to hormonal changes that slow down gallbladder function.
Symptoms of gallstones
Many people with gallstones do not experience symptoms, a condition known as “silent” gallstones. However, when symptoms do occur, they can be uncomfortable and severe. The most common symptom is sudden, intense pain in the upper right abdomen or the centre of the abdomen, which may radiate to the back or shoulder blades and can last from several minutes to hours. Gallstone attacks may also cause nausea or vomiting, especially after consuming fatty foods. If a gallstone blocks the bile duct, it can result in jaundice, leading to yellowing of the skin and eyes. In cases where an infection or inflammation occurs, symptoms like fever and chills may also develop.
Diagnosis of gallstones
If gallstones are suspected based on symptoms, a doctor may recommend several tests to confirm the diagnosis. Ultrasound is the most common and non-invasive imaging test used to detect gallstones. Blood tests may also be conducted to identify signs of infection, inflammation, or liver function abnormalities caused by blocked bile ducts. For more detailed imaging, a CT scan or MRI can be used to provide clear images of the gallbladder and bile ducts, helping to detect any complications from gallstones. Additionally, a HIDA scan may be performed to evaluate gallbladder function by tracking the flow of bile using a radioactive tracer.
Treatment options
Treatment for gallstones depends on the severity of symptoms and the size or number of stones. Asymptomatic individuals may not require treatment, while others with symptoms might need medical or surgical intervention. Non-surgical treatments include medications that can help dissolve cholesterol gallstones, though this process is slow and may take months or years. Sound waves may also be applied to break gallstones into smaller pieces that pass naturally, but it’s only suitable for certain cases. Surgical treatments include the removal of the gallbladder, which is the most common option for symptomatic gallstones, which can be done through open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery. For gallstones blocking the bile ducts, stones can be removed without removing the gallbladder.
Preventing gallstones
While some risk factors for gallstones, such as age and genetics, are beyond control, adopting certain dietary and lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight is key, as obesity is a major risk factor for gallstones. However, it’s important to avoid rapid weight loss, which can increase the risk. A gradual, steady approach to weight management through regular exercise and a balanced diet is best.
- Healthy diet: Following a low-fat, high-fibre diet is another important preventive measure. Whole grains like brown rice and oats, along with fruits and vegetables such as leafy greens, berries, and carrots, should be incorporated into meals. Additionally, choosing healthy fats from sources like olive oil, avocados, and nuts can promote gallbladder health and reduce the likelihood of gallstones. Limiting refined carbohydrates and sugary foods, such as white bread and pastries, is also beneficial for promoting better digestion and gallbladder function.
- Eating and drinking: To prevent gallstones, it’s also crucial to avoid skipping meals, as fasting or missing meals can reduce gallbladder contractions, leading to bile concentration and gallstone formation. Regular, balanced meals support healthy gallbladder function. Staying hydrated is equally important, as drinking enough water helps the body process fats and cholesterol more efficiently, reducing the risk of gallstones.
- Lifestyle changes: In addition to dietary changes, adopting healthy lifestyle habits can help in preventing gallstones. Regular exercise not only aids in maintaining a healthy weight but also promotes overall digestive health. Quitting smoking is another essential step, as smoking is linked to an increased risk of gallstones and other digestive disorders. While moderate alcohol consumption may offer some health benefits, excessive drinking can raise the risk of gallstones and liver-related complications, making it important to limit alcohol intake.
When to see a doctor?
It is imperative that you consult a physician if you have severe stomach pain, particularly after meals, or if you observe any symptoms of jaundice. More severe side effects such as pancreatitis, bile duct obstructions, or gallbladder infections can be avoided with early gallstone identification and treatment. When it comes to gallstone diagnosis and treatment, a gastroenterologist is essential. To find gallstones and determine how severe they are, they can do imaging tests like ultrasounds. Depending on the circumstances, a gastroenterologist might suggest medicine to dissolve smaller stones, lifestyle modifications, or, in more extreme cases, a referral to a surgeon for gallbladder removal. In order to guarantee that patients receive thorough treatment for gallstone-related concerns, a gastro doctor Ahmedabad, such as one at Mission Gastro Hospital, assists in managing symptoms including discomfort, nausea, and digestive problems.